Cavity Walls Overview!
In this article, you'll discover why cavity walls are commonly used in buildings and how to identify them in the majority of properties.
We'll also cover the pros and cons of having cavity walls, and the myths around them answering some common questions along the way?
Knowing how to quickly spot cavity walls and identify potential issues, can save you thousands of pounds.
In addition to significantly improving the energy efficiency and comfort of your home.

What is Cavity Wall?
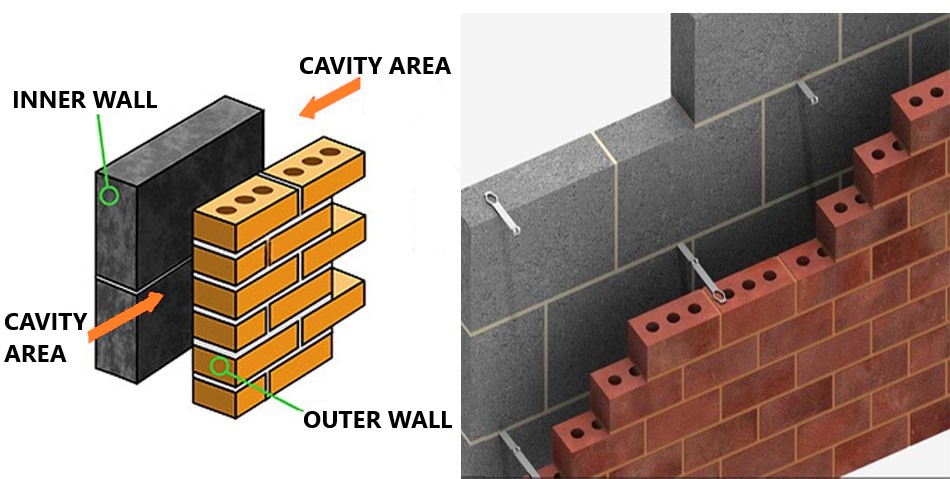
A cavity wall consists of two separate walls, usually made of brick or block, with a gap (or cavity) between them.
Cavities are typically between 50mm and 150mm wide and serves multiple purposes, primarily insulation & moisture protection.
How To Spot Cavity Walls?

Other Signs & Ways?
Use a door or a window to measure the distance between the outside wall and the inside wall. If this is more than 260mm thick, it's probably a cavity wall.
Look for drill hole patterns / scars on the brick work, where insulation has possibly been pumped into the walls in the past
Hard to heat property, with damp issues and condensation issues. Especially if a modern property which could be a sign of defective cavity insulation needing extracted.
Contact a professional to undertake a survey, we supply Cavity Wall Insulation In Northern Ireland, and free surveys!
Why Do We Have Cavity Walls?
The primary function of a cavity, is to serve as a barrier between the exterior and interior walls.
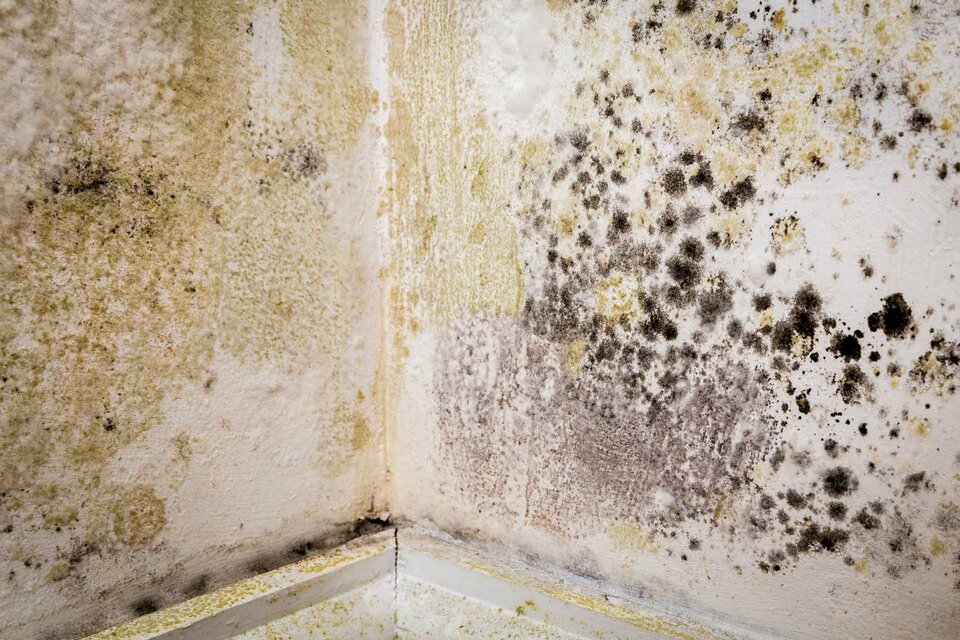
This barrier prevents moisture from transferring from the outer wall to the inner wall, protecting the interior inside decorated walls from the damp & mold.

The cavity wall method was introduced in the 1920s, however not all homes built from this period onwards have cavity walls.
What Walls Were Used Before Cavities?
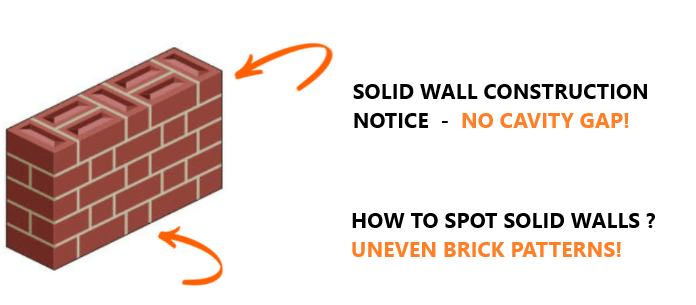
Solid walls, which lack cavities, were common before cavity wall construction gained popularity during the housing boom of the 1930s and 1940s.
By the 1990s, cavity walls became mandatory for new builds in the UK. Unlike cavity walls, solid walls offer no protection or thermal airflow between the exterior and interior, leading to several issues.
Such as decaying brickwork & rising damp due to outdated construction practices. These homes are harder to heat and challenging to upgrade with modern insulation, making them less energy-efficient and more prone to structural problems..
Advantages of Cavity Walls
Thermal Insulation
The gap between the inner and outer walls reduces heat transfer, helping to keep buildings warmer in winter & cooler in summer.
Moisture Protection
The cavity acts as a barrier, this ensures any water entering the outer wall does not reach the inner wall.
Sound Insulation
The structure of cavity walls provides sound insulation, reducing the amount of external noise that enters the home :-)
Structural Stability
Increased structural stability of any building. The two walls, tied together with metal connectors, will be sturdy plus long lasting.
Energy Efficiency
By improving thermal insulation, cavity walls contribute to better energy efficiency all year round. In addition reducing utility bills and minimize the environmental impact of heating and cooling a building.
Versatile Construction
Cavity walls offer flexibility in construction. They can be built with various materials, including bricks, blocks, and insulating materials, allowing for a wide range of architectural designs and finishes.
Disadvantages of Cavity Walls
Construction Complexity
Cavity wall construction is more complex compared to solid wall construction.
It requires precise alignment and installation of the inner & outer walls, proper placement of wall ties, and ensuring the cavity remains clear of mortar droppings & debris.
This can lead to longer build times plus increased labor costs, during the intial build process.
Insulation Challenges
While cavity walls can be insulated, retrofitting insulation into existing cavity walls needs to be undertaken by professionals.
Poorly installed insulation can lead to gaps and cold spots, reducing the effectiveness of the insulation and potentially causing condensation issues within the cavity.
Seeking professional advice can help you make the best decision regarding cavity health issues.
Moisture Penetration
Although cavity walls are designed to prevent moisture penetration, they are not completely foolproof.
If the outer wall is damaged or if the cavity is not properly constructed, water can still find its way into the cavity and eventually reach the inner wall, causing damp problems inside the building.
Thermal Bridging
This is the most common issue we encounter, If not properly constructed, or wall ties fail over time cavity walls can suffer from thermal bridging.
This occurs when components that span the cavity, such as wall ties or mortar droppings, create a conductive path for heat to escape.
Thermal bridging can significantly reduce the wall's overall thermal performance.
Inspection & Repairs
Inspecting and repairing issues within the cavity, such as replacing corroded wall ties or removing debris, can be difficult and costly.
These repairs often require specialized equipment and expertise.
Limitations in Certain Climates
In areas with extremely high wind-driven rain or very cold climates, cavity walls may not provide sufficient insulation or moisture protection on their own.
Additional measures, such as thicker insulation or external cladding, may be necessary, further increasing costs and complexity.
What Types Insulation Are Inside Cavities?
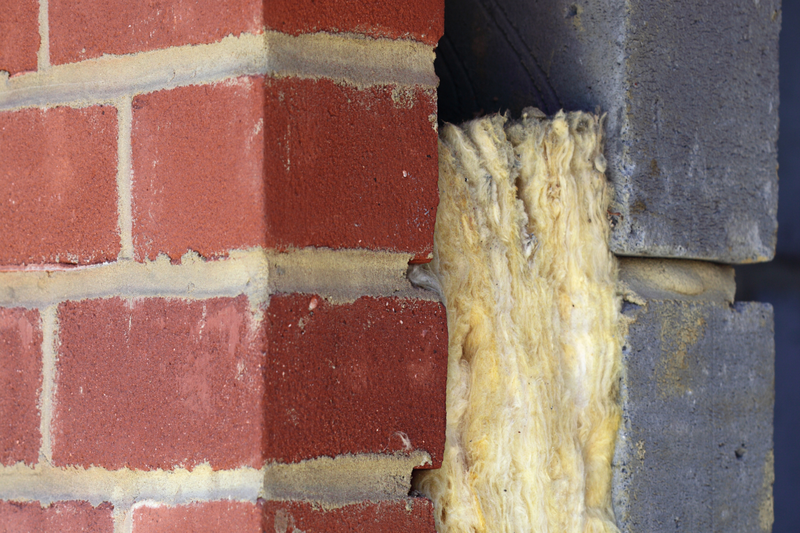

Historically cavity walls have had many different types of materials fitted, such as:
Mineral wools / Fibres
Cavity Foam Insulation
Polystyrene beads Current trend
Rigid Insulation Boards
Cavity Batts
What's The Best Cavity Wall Insulation?
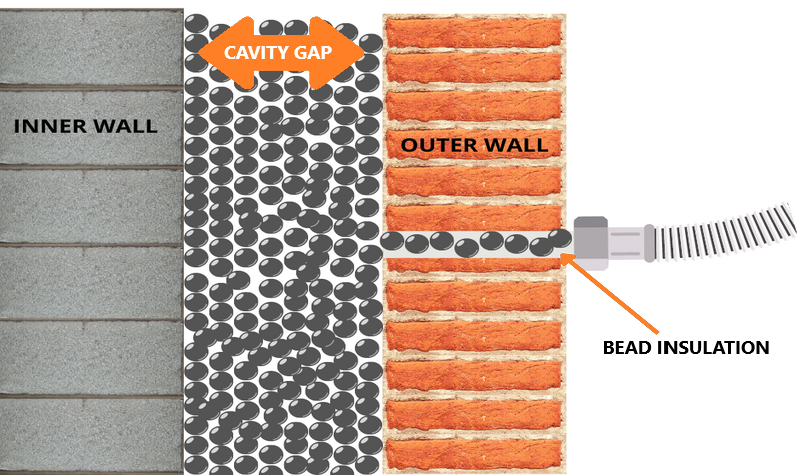
The best cavity wall insulation to avoid damp, which causes all the main issues is polystyrene beads! We supply & fit this type of Cavity Wall Insulation in Northern Ireland.